0.写在前面的话
本文参考于:learnopenglCN特别感谢此项目维护者们的辛勤付出。觉得有帮助可以给项目点个Star
由于上述项目是从英文版本翻译而来,在观看时总会有一种不太流畅的感觉,同时因为上述文章内的介绍过于详尽,并且有部分地方描述存在较模糊的情况,故编写此文章。
此篇文章将专注于快速配置好开发环境,对于部分概念不予解释,如需详尽了解请参考上述链接。
本文章仅介绍基于Visual Studio2022+glfw+glad(64位)+c++的快速配置,且是基于项目的,也就是每个项目都需要重新配置一次。个人不推荐直接修改整个生产环境,因为你不知道会在其他开发时会遇到什么别的问题(也可能是我多虑),如果不符合您的预期请另寻其他教程,或评论区留言。
1.环境及资料准备
环境:
- Windows11电脑
- c/c++
- glfw
- glad
- Visual Studio2022
资料准备:
- 下载glfw
- 下载glad
- 安装配置vs2022请参考我早期文章,这里不过多赘述VS studio2022通俗易懂的安装及使用教程
先进行第一步下载glfw
百度搜索glfw进入官网或直接点击glfw官网
点击右上角Download
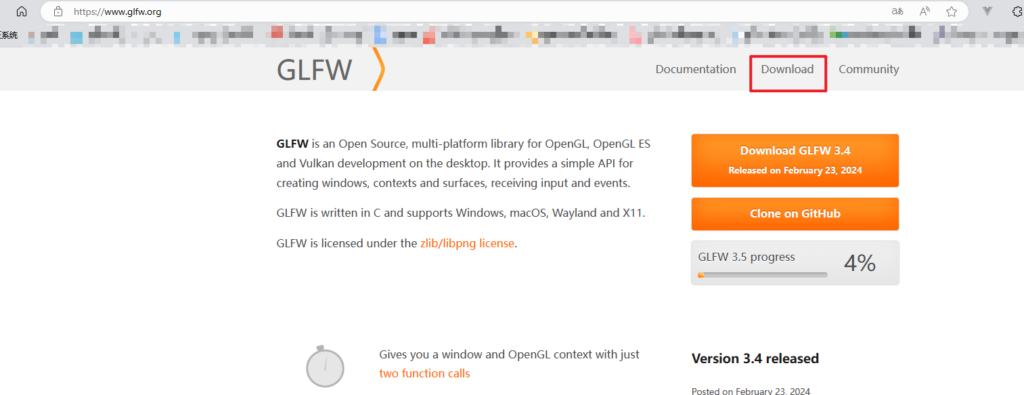
选择64位并下载
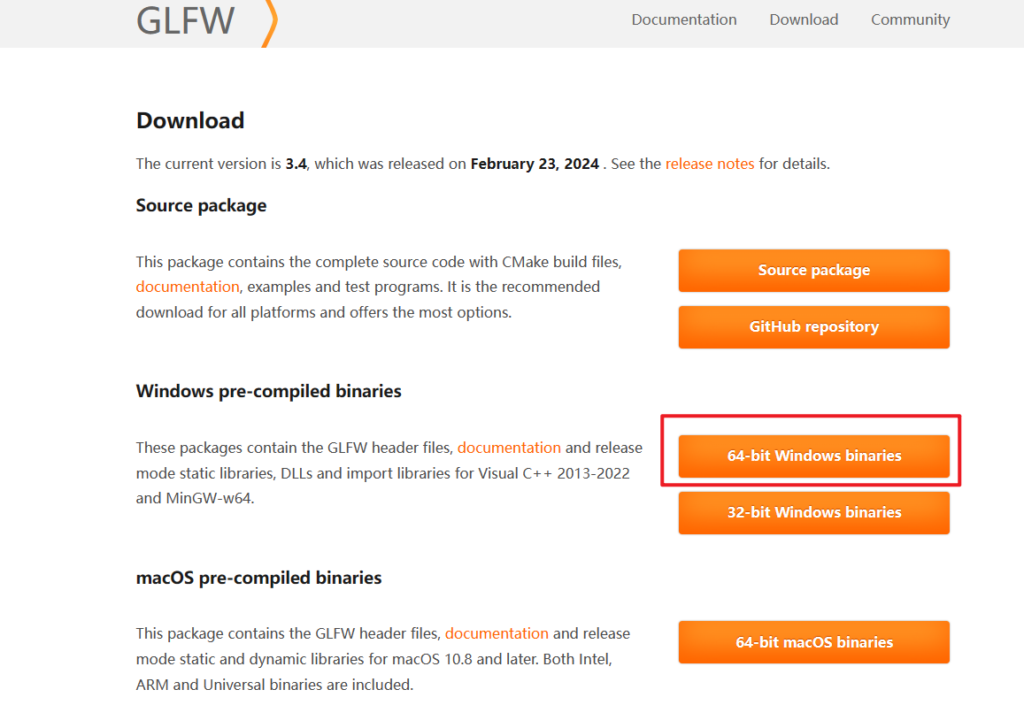
下载后类似下图
![]()
解压备用。
下载glad
百度搜索glad或直接点击Glad在线服务
无法打开或加载缓慢请尝试更换您的网络环境。
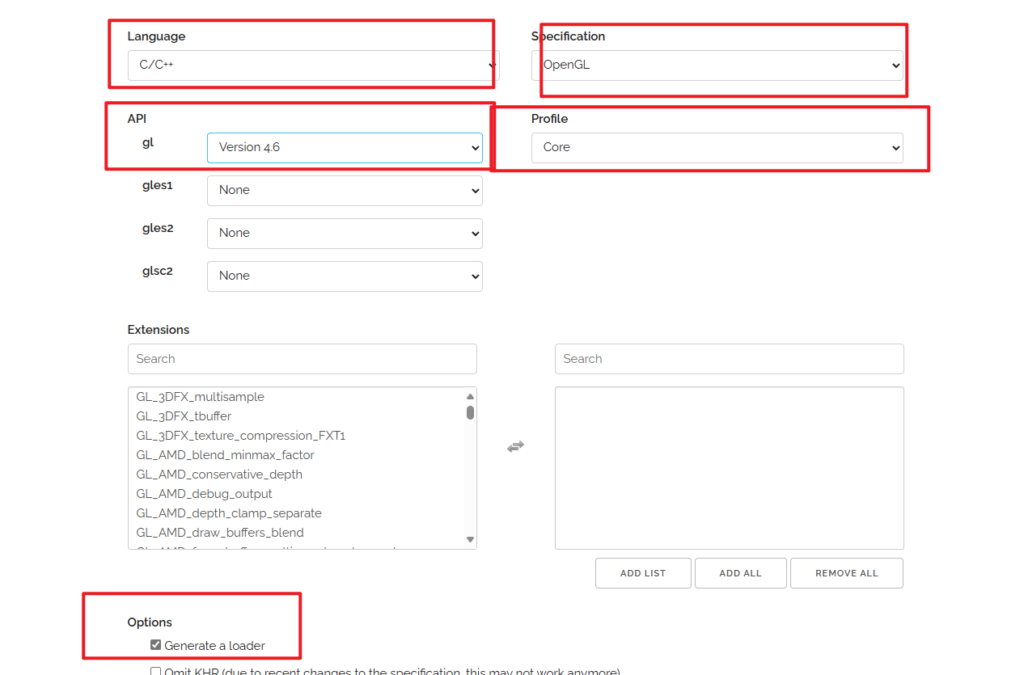
- 将语言(Language)设置为C/C++。
- 在API选项中,选择3.3以上的OpenGL(gl)版本最新版本也可。
- 将模式(Profile)设置为Core,并且保证选中了生成加载器(Generate a loader)选项。
- 先暂时忽略扩展(Extensions)中的内容。点击生成(Generate)按钮来生成库文件。
如下图:
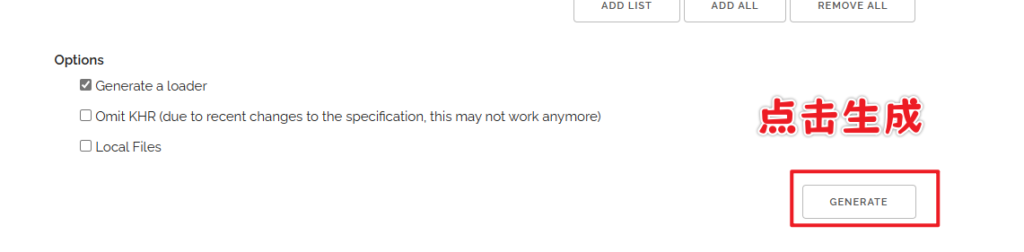
您将被跳转到如下界面:
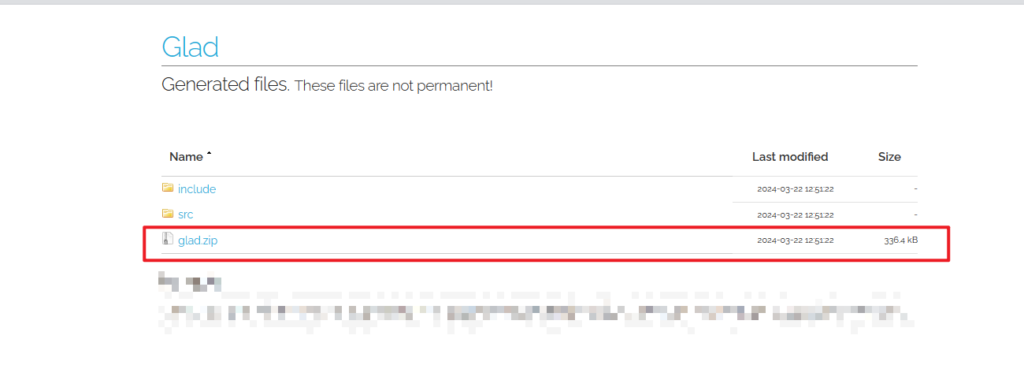
点击下载glad.zip即可,同样解压备用。
2.项目配制
创建项目
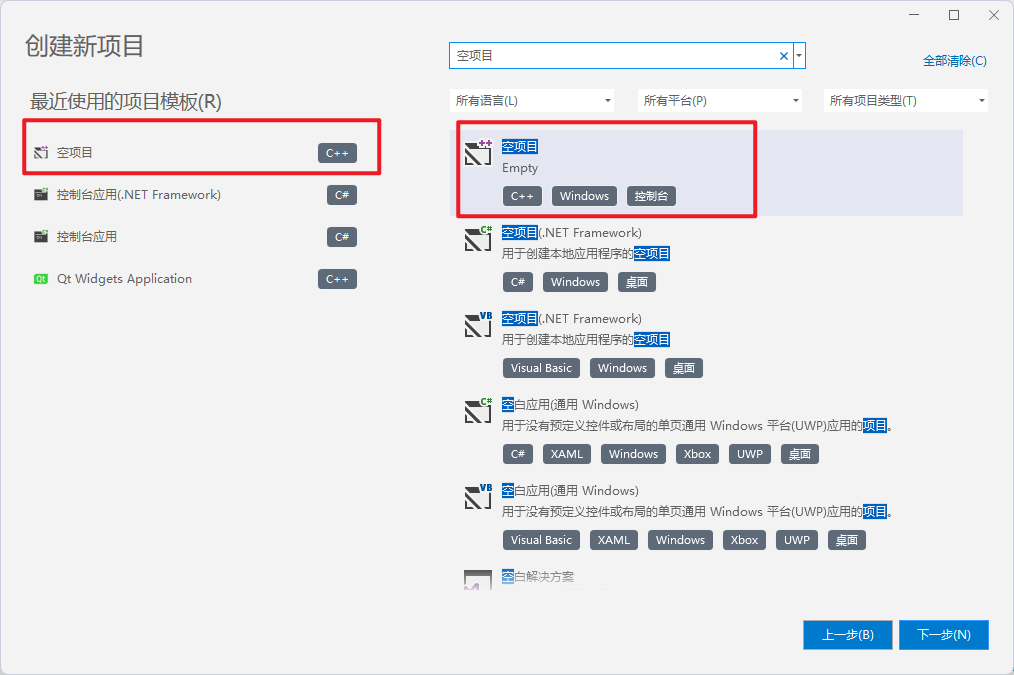
打开vs2022,点击创建新项目,选择空项目,和正常创建c++项目一致,并且为您的项目取名字(建议不要带有中文),我们这里取为opengltest
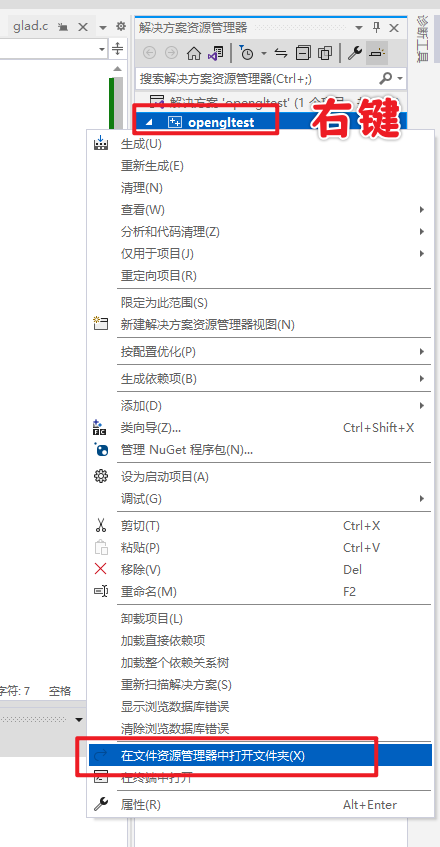
接下来打开项目目录(在解决方案资源管理器中右键项目名称,选择在文件资源管理器中打开文件夹)。
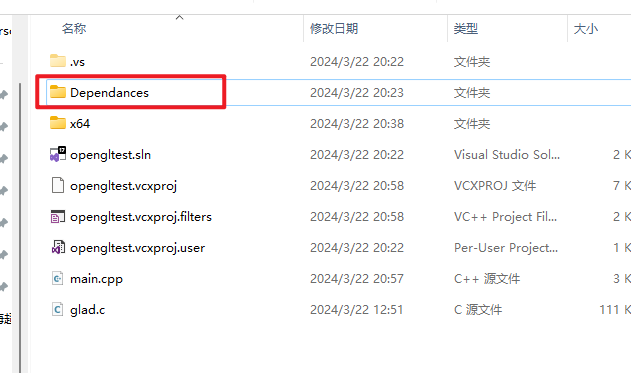
在项目文件夹内新建一个文件夹,并重新命名(同样建议不要使用中文),我这里使用Dependances
文件复制
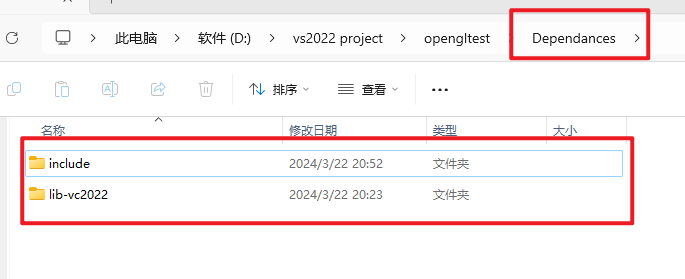
将我们先前解压好的glfw文件夹内的include和lib-vc2022复制到刚刚创建的Dependances文件夹内。
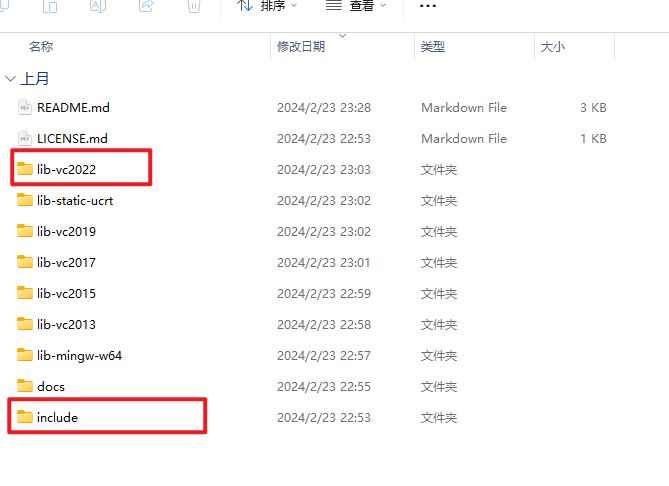
如下图
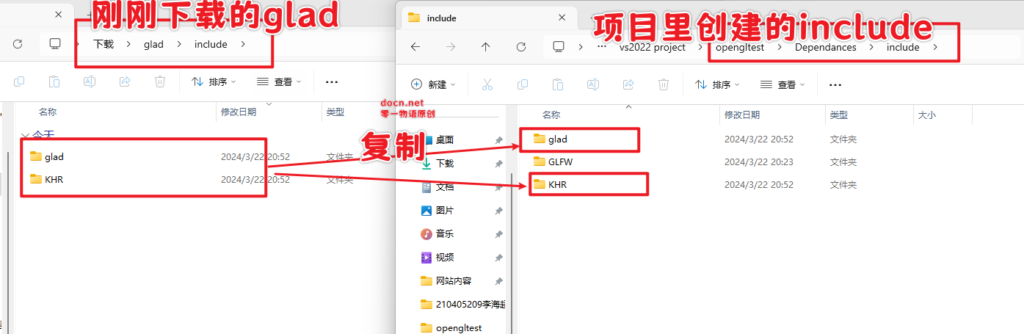
同时,我们将刚刚准备好的glad文件夹内的include内的两个文件夹(分别为KHR和glad)复制到我们刚刚在项目中创建的Dependances里的include里。
项目属性配置
现在,我们回到vs2022编辑器内,右键项目名称,选择属性
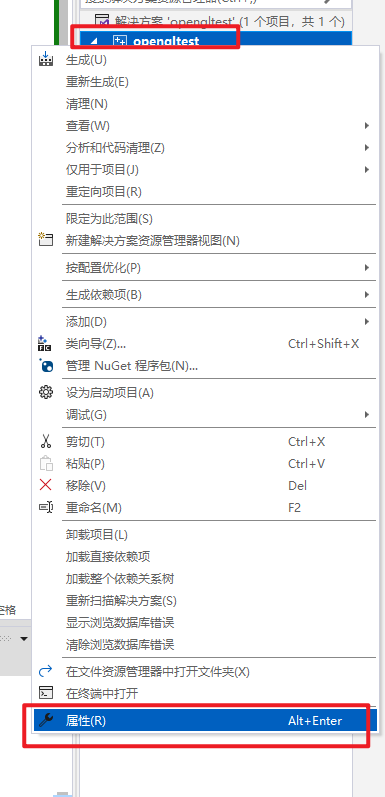
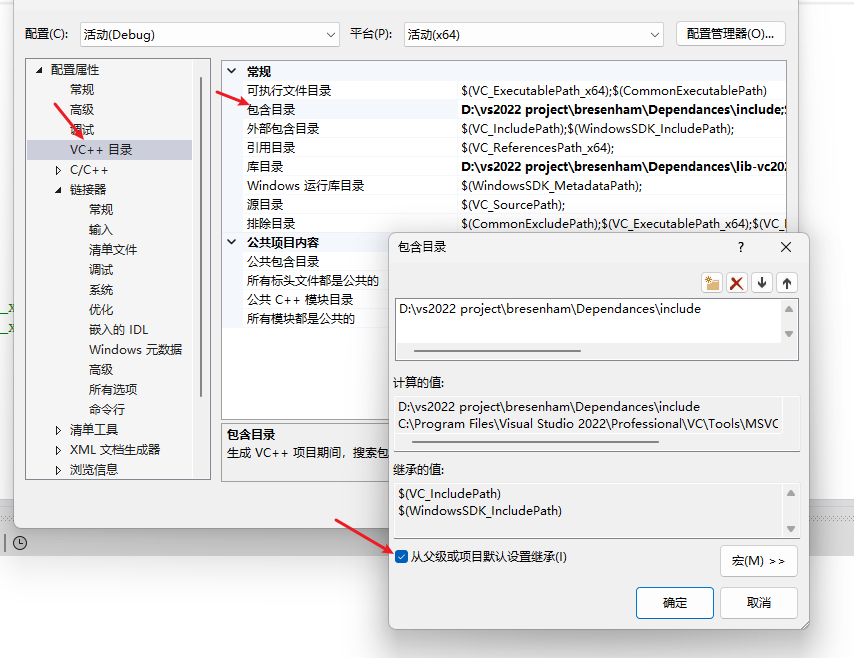
选择VC++目录(VC++ Directories),
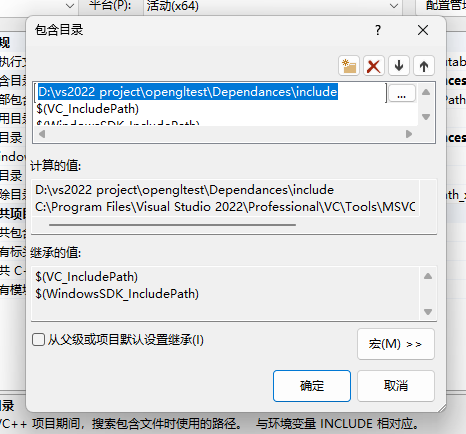
将包含目录(Include Directories)填写上我们刚刚在项目里创建的Dependances的include文件夹完全路径
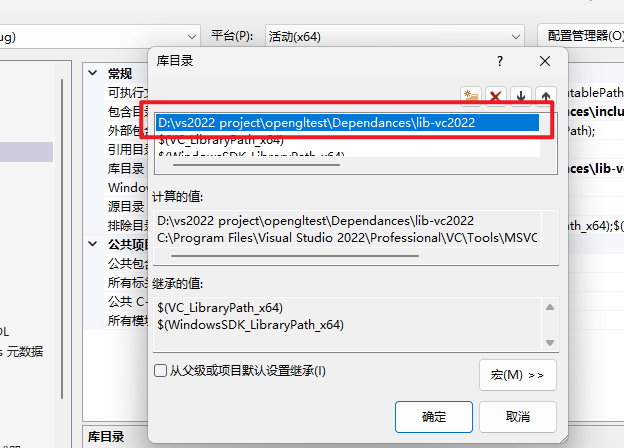
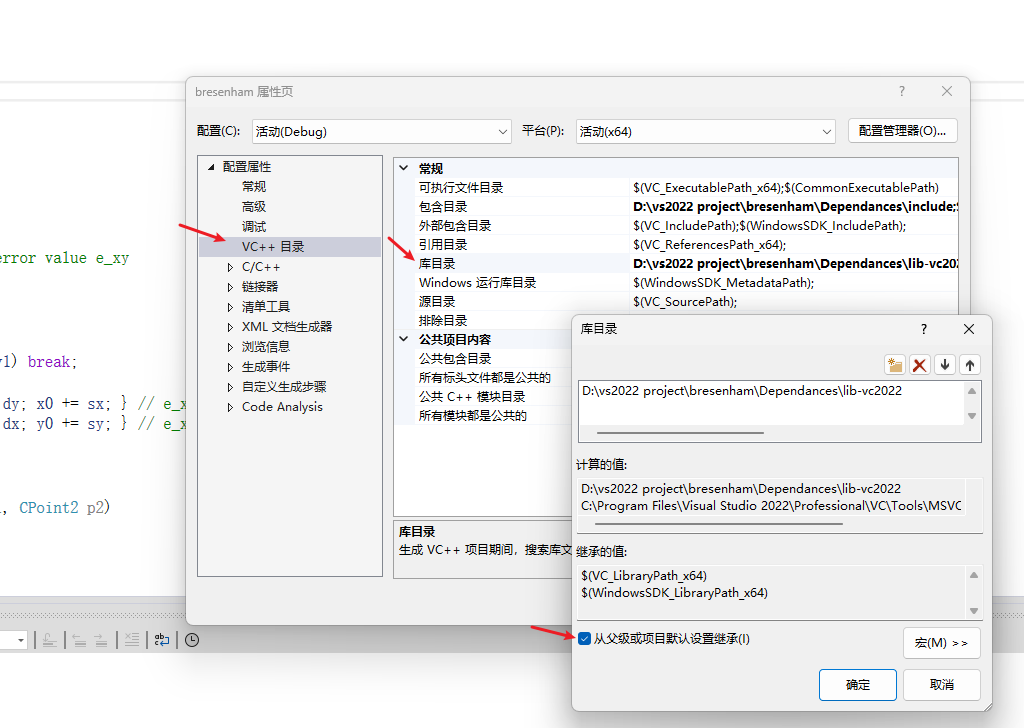
在库目录(Library Directories)填写Depnedances里的lib-vc2022文件夹路径
可以直接点击填写,点击填写,但在结束之后需要加上引文的;分号
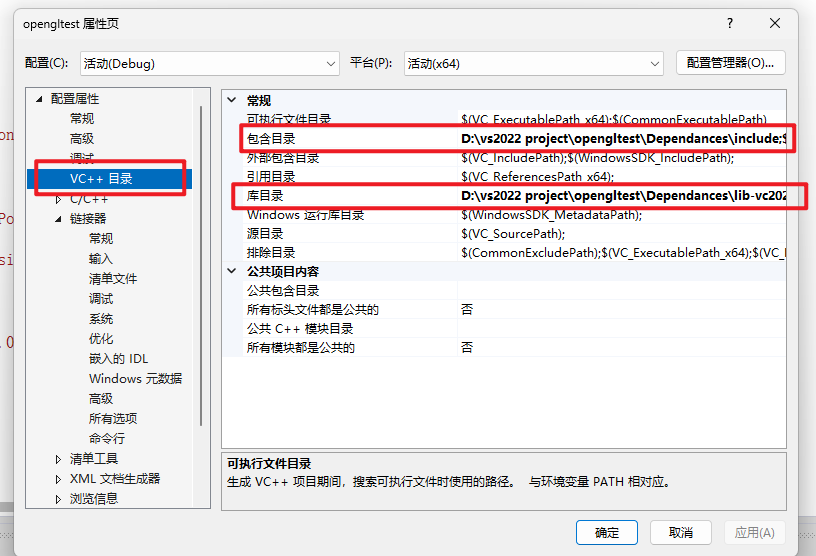
也可以点击后面的下拉箭头,选择编辑
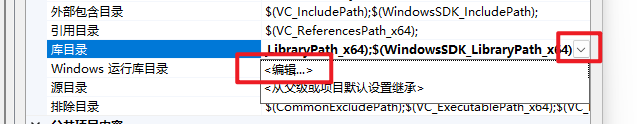
一行一个链接填写即可。
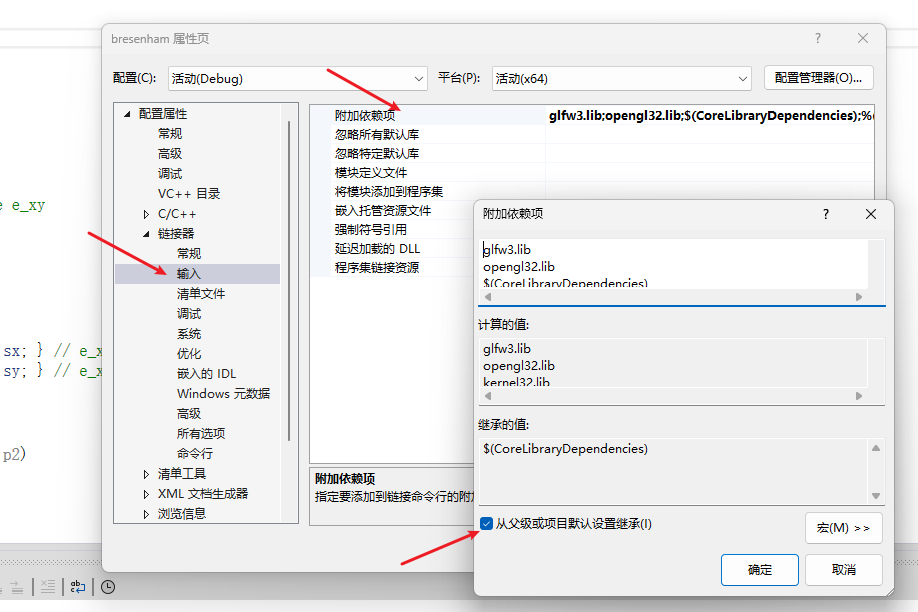
最后需要在链接器(Linker)选项卡里的输入(Input)选项卡里添加glfw3.lib和opengl32.lib
使用分号隔开。
如下图:
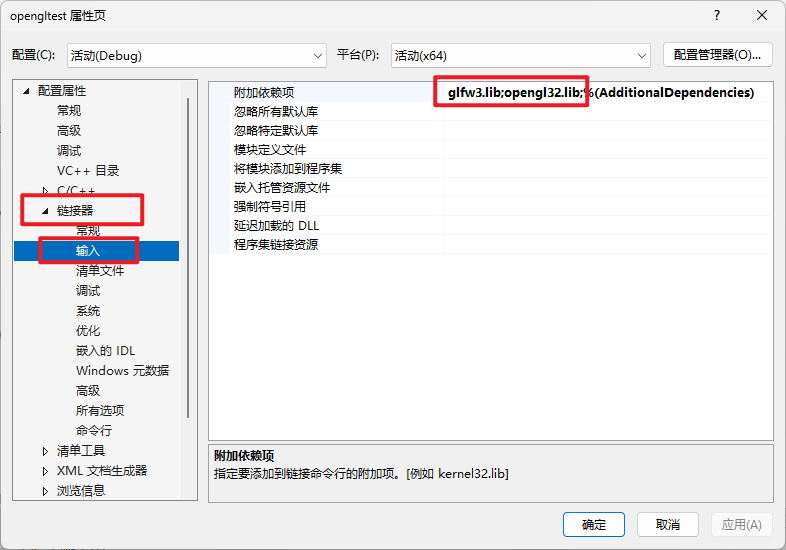
最后我们将刚刚下载的glad文件夹内的src里的glad.c添加到项目目录里
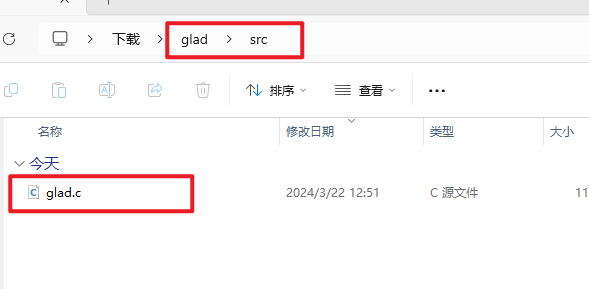
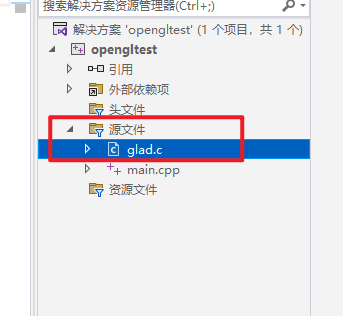
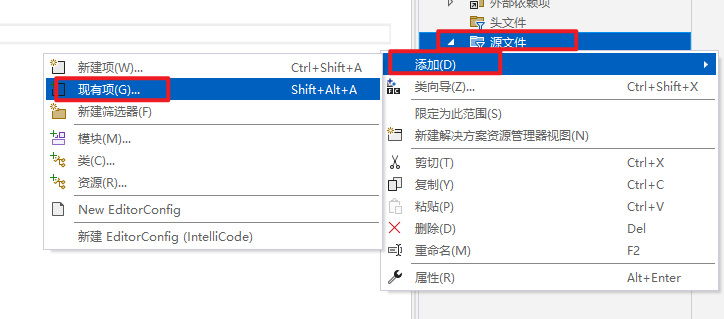
添加方法(写给不会添加现有代码的同学)
右键源文件,添加,现有项,在新窗口中找到解压的glad.c即可。
请将vs2022上方的运行平台改为x64,如果opengl配好后不报错,但不能运行的请重启电脑
如果出现“无法打开文件“opengl32.lib“,请勾选以下三个目录的从父级或项目默认设置继承
测试
现在,新建一个.cpp输入以下代码来尝试一下吧。
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <iostream>
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
const char* vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" gl_Position = vec4(aPos.x, aPos.y, aPos.z, 1.0);\n"
"}\0";
const char* fragmentShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"out vec4 FragColor;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" FragColor = vec4(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.2f, 1.0f);\n"
"}\n\0";
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// build and compile our shader program
// ------------------------------------
// vertex shader
unsigned int vertexShader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertexShader, 1, &vertexShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertexShader);
// check for shader compile errors
int success;
char infoLog[512];
glGetShaderiv(vertexShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::VERTEX::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// fragment shader
unsigned int fragmentShader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragmentShader, 1, &fragmentShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragmentShader);
// check for shader compile errors
glGetShaderiv(fragmentShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FRAGMENT::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// link shaders
unsigned int shaderProgram = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
glLinkProgram(shaderProgram);
// check for linking errors
glGetProgramiv(shaderProgram, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if (!success) {
glGetProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::PROGRAM::LINKING_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
glDeleteShader(vertexShader);
glDeleteShader(fragmentShader);
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
float vertices[] = {
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top right
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top left
};
unsigned int indices[] = { // note that we start from 0!
0, 1, 3, // first Triangle
1, 2, 3 // second Triangle
};
unsigned int VBO, VAO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
// bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s), and then configure vertex attributes(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the vertex attribute's bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// remember: do NOT unbind the EBO while a VAO is active as the bound element buffer object IS stored in the VAO; keep the EBO bound.
//glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// You can unbind the VAO afterwards so other VAO calls won't accidentally modify this VAO, but this rarely happens. Modifying other
// VAOs requires a call to glBindVertexArray anyways so we generally don't unbind VAOs (nor VBOs) when it's not directly necessary.
glBindVertexArray(0);
// uncomment this call to draw in wireframe polygons.
//glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// draw our first triangle
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glBindVertexArray(VAO); // seeing as we only have a single VAO there's no need to bind it every time, but we'll do so to keep things a bit more organized
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
// glBindVertexArray(0); // no need to unbind it every time
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
glDeleteProgram(shaderProgram);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow* window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}如果没问题的话应该会显示出一个矩形。
接下来,开启你的opengl之旅。
建议学习网站:learnopenglCN,链接在文章开头。
我们下个教程见,拜!
再次更新,部分笔记本外接显示器时设置为仅外接显示器显示会导致opengl无法正常绘制,解决办法是用笔记本自己的显示器或者是将显示模式更改为复制,即都亮的情况下。我也还不知道为什么外接显示器不会正常绘制。

- 本博客所拥有的文章除特别声明外,均默认采用 CC BY 4.0 许可协议。
- 文章部分内容可能来源于公共网络,如有侵权,请联系博主在核实后进行修改或删除。











- 最新
- 最热
只看作者